Laser safety
Due to the special properties of laser radiation and the resulting biological and physical effects, special protective and precautions are required when using lasers.
For the determination of the measures to be taken in each individual case, the lasers are divided into classes according to their risk potential.
Decisive for the classification of the laser devices in classes 1, 1 m, 2, 2 m, 3 R, 3 B and 4 are the accident prevention regulation "laser radiation" BGV B2 and the din standard EN 60825-1 (vde 0837 Part 1).

The accessible laser radiation is harmless.

The accessible laser radiation is harmless as long as no optical instruments such as magnifying glasses or binoculars are used.

The available laser radiation is only visible in the spectral range (400 nm to 700 nm). It is also harmless to the eye for short duration of irradiation (up to 0.25 s). A longer irradiation is prevented by the natural Lidschluss reflex.

Like Class 2 as long as no optical instruments such as magnifying glasses or binoculars are used.

The accessible laser radiation is dangerous for the eye.

The accessible laser radiation is dangerous for the eye and in special cases also for the skin.

The accessible laser radiation is very dangerous to the eye and dangerous to the skin. Diffuse scattered radiation can also be dangerous. The laser radiation can cause fire or explosion hazard.
*) Anmerkung zu Laserklasse 2 und 2M: Durch wissenschaftliche Untersuchungen (FH Köln) wurde festgestellt, dass der Lidschlussreflex (dieser tritt im übrigen innerhalb 0,25 s auf; eine längere Bestrahlung schädigt das Auge) nur bei <20 % der Testpersonen gegeben war.
As a rule, the presence of the Lidschluss reflex for the protection of the eyes must not be assumed.
Therefore, if laser radiation of Class 2 or 2m meets the eye, you should deliberately close your eyes or turn away immediately. It should also be noted that the Lidschluss reflex only occurs when the light is visible.
Laser radiation in the infrared region, for example, does not lead to a Lidschluss because the radiation is not perceived by the eye. Therefore, a particularly careful handling of invisible laser radiation is advisable.
Laser emissions:
Why laser smoke extraction is essential
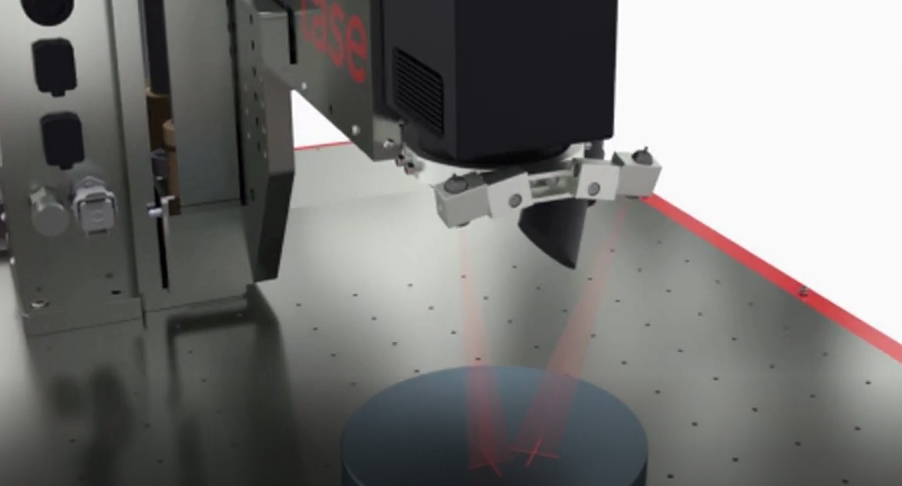
Laser smoke is produced by the laser when engraving or marking in direct material processing.
Depending on the materials used, the composition of the laser smoke and its properties can be seen.
The processing of metals often produces aerosols (suspended particles) which contain heavy metals and can lead to poisoning.
Furthermore, some metals (e.g. chromium) are suspected to have carcinogenic effects. Therefore, in addition to a dense enlargement, which is already required for laser protection reasons for Laser Class 1 and prevents a spread of the laser smoke, also a special laser smoke extraction.
The processing of organic materials, such as plastics, wood, textiles and leather, also produces pollutants.
Due to the high energy of the laser, reactions take place, whose products can be harmful to health.
The processing of plastics such as PTFE or PVC (Polyvinylchloride) is particularly problematic. This can result in hydrogen chloride or hydrogen fluoride, which are both toxic and corrosive.
Laser dust is extremely problematic due to the small size of the particles that can penetrate the lungs and are even absorbed into the blood.
The operator is responsible for the safe removal and disposal of pollutants in accordance with local, national and regional threshold limits.
Thanks to the technical conception and the integrated suction system developed especially for laser smoke, our laser systems ensure the highest possible protection of the employees.